Cultivation of Green Gram ( Moong) ; A complete Information Guide
Cultivation of Green Gram ( Moong); A complete Information Guide;
Green Gram or Moong (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) belongs to the family Leguminosae and subfamily Papilionaceae. It is a small herbaceous annual plant growing to a height of 30 to 100 cm with a slight tendency to twining in the upper branches.
Vernacular Names of Green Gram;
- Hindi; Mung/Moong Dal
- Bengali;Mung, and Mmug dal
- Gujrati; Mug
- Marathi; Moog dal
- Malayalam; Cheru payaru
- Kannada; Hesar Kalu
- Telugu;Pesallu/Pesara pappu
- Tamil; Paasi paruppu
Importance of Green Gram or Moong beans;
- Green gram (moong) is an excellent source of high-quality protein. It contains about 25 percent protein.
- Moong is consumed as whole grains as well as dal in a variety of ways in homes.
- Sprouted whole moong is used in south India for preparing curry or a savory dish.
- It is used mostly as dal in northern India. It is supposed to be easily digestible and hence is preferred by patients.
- Moong halwa is said to be very nutritious.
- Moong dal (split) and dehusked fried in fat go very well with tea or drinks as a snack.
- When moong beans are allowed to sprout, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is synthesized. The amount of riboflavin and thiamine are also increased
- Moong is also used as a green manuring crop. Being a leguminous crop, it has the capacity to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- It also helps in preventing soil erosion. Being a short-duration crop it fits well in many intensive crop rotations.
- Moong can be used as feed for cattle.
- After harvesting the pods, green plants are uprooted or cut from ground level and chopped into small pieces and fed to the cattle.
- The husks of the seed can be soaked in water and used as cattle feed.
Nutritive Value of Green Gram or Moong Bean ;
|
Nutrient |
Value |
Nutrient |
Value |
|
Calories |
347 |
Sodium |
15mg |
|
Protein |
24.0 g |
Potassium |
1.24mg |
|
Fat |
1.20 g |
Magnesium |
47% of RDI |
|
Fiber |
16.0 g |
Zinc |
3.35 mg |
|
Carbohydrate |
63.0 g |
Vitamin A |
2% of RDI |
|
Calcium |
13%of RDI |
Vitamin C |
8% of RDI |
|
Phosphorus |
16% of RDI |
Vitamin B6 |
20% of RDI |
|
Iron |
37% of RDI |
Folate (B9) |
89% of RDI |
(RDI; Reference Daily Intake )
Major Health Benefits of Green Gram (Moong Bean)
- Excellent Source of High-Quality Protein
- Provides Detoxification Benefits
- Lowers Cholesterol & Heart Disease Risk
- Lowers High Blood Pressure
- Easiest to Digest Among all Beans
- May Help Fight Cancer
- May Prevent & Possibly Treat Diabetes Type 2
- Decreases PMS Symptoms
- Helps Reduce Weight & Fights Obesity
- Boosts Immunity & Protects Against Infections
- Improves Skin Health
Climatic Requirements For Moongbean Cultivation ;
- Green gram (moong) is best suited to areas having an annual rainfall of 60 to 75 cm.
- Moong is considered to be the hardiest of all pulse crops.
- It requires a hot climate and can tolerate drought to a great extent.
- It can be grown from sea level to an elevation of 2000 meters.
- It is grown in Kharif and summer seasons in northern India but in the south and southwest, it is also grown as a Rabi season crop.
Soil Requirements For Moongbean Cultivation ;
- Moong is a crop that is grown on a variety of soils from red-laterite soils of south India to black cotton soils of Madhya Pradesh and sandy soils of Rajasthan.
- A well-drained loamy to sandy loam soil is best suited for moong cultivation.
- Saline and alkaline soils are not suitable for moong cultivation.
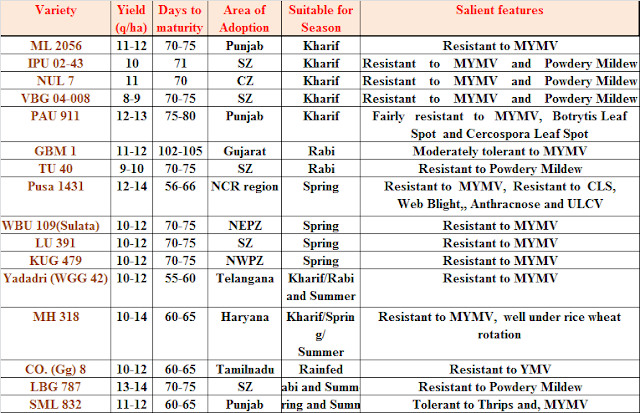
Important Varieties of Green Gram or Moong Bean;
Rotations and Mixed Cropping ;
4.Moong – potato
Field Preparation For Green Gram (Moong Bean) Cultivation;
- The field is prepared by giving two or three cross harrowings followed by planking. The field should be well leveled and free from weeds, For the summer season crop, give a pre-irrigation immediately after harvesting of Rabi crop
- When the field comes in condition, prepare it by giving two to three ploughings by a local plough or harrowings.
- Each ploughing/harrowing should be followed by planking to make the field leveled and to minimize the loss of moisture by evaporation from the soil surface.
Seed and sowing of Green Gram (Moong Bean);
(1) Time of Sowing ;
(2) Seed Rate And Spacing;
(a) Kharif season;
Management of Manures and Fertilisers in Green Gram(Moongbean);
- Moong is generally grown on the basic fertility of oil. However, if available 8-10 tonnes of compost or farmyard manure should be applied before 15 days of sowing.
- If organic manure is not available apply 15-20 kg nitrogen and 40 to 50 kg P205 per hectare at the time of sowing.
- If available, drill 100 kg of diammonium phosphate to meet the requirement of both nitrogen and phosphorus.
- The fertilizer should be applied by drilling either at the time of sowing or just before sowing in such a way that they are placed about 5-7 cm below the seed.
Water Management in Green Gram(Moongbean);
- For rainy season crops, irrigation is not needed but drainage is very important. There should be adequate drainage in the field because this crop is sensitive to waterlogging conditions.
- For Rabi and summer crops, five to six irrigations may be given. The field should be irrigated when soil is seen as deficient in moisture. During summer, because of high temperature and low relative humidity, more irrigations are needed as compared to the Kharif crop.
- The first irrigation should be given about 20-25 days after sowing. The subsequent irrigations should be given at an interval of 12-15 days. No irrigation should be given when the crop is in the full bloom stage.
Weed Control in Green Gram(Moongbean);
- Two weddings should be given to keep the crop free from harmful weeds.
- The first wedding should be done 20-25 days after sowing and the second 45 days after sowing.
- Weeds do not pose a serious problem during summer. However, one weeding should be done after irrigation. During the rainy season.
- weeds can be controlled by the use of chemicals too. Use Basalin 1 kg a.i. per hectare in 800-1000 liters of water as a pre-planting spray. It should be well incorporated in the soil before sowing.
Diseases and Pest Management in Green Gram (MoongBean)
Disease Management ;
a) Yellow Mosaic;
The symptoms of the disease appear within a month after sowing. These are first visible in the form of yellow, diffused, round spots scattered on the leaf lamina. These spots expand rapidly and the leaves show yellow patches alternating with the green color of the leaves. The newly emerging leaves, after initial symptoms, show these symptoms right from the beginning. The affected leaves later turn completely yellow and get reduced in size.
Control Measures;
The symptoms of this disease appear in the form of irregular light green areas, alternating with normal green areas. The leaves emerging after the initial symptoms become deformed, reduced in size and their margins show upward rolling. Later, these young leaves show the raising of the interveinal areas appearing in the form of blisters.
Control Measures
c) Leaf Crinkle;
The symptoms are visible first in the third leaf after three to four weeks of sowing. These are characterized by the enlargement of leaves followed by their crinkling. Later the leaves become thicker and leathery. The affected plants, however, do not die till the harvest of the crop.
Control Measures;
(1) Sow the seeds obtained from healthy plants only.
d)Leaf Curl ;
It is a viral disease. The initial symptoms of the disease are seen within three weeks of sowing as chlorosis around the lateral vein near the leaf margin in young plants. The affected leaves show curling of margins downwards while the veins on the undersurface of the leaf show reddish-brown discoloration. Further growth of the affected plant is stopped. Such plants can be recognized by their typical stunted growth.
Control Measures;
Spray the crop with Metasystox (0.1%). Two to three sprays at 10 days intervals are sufficient.
e) Seed And Seeding Rot
Several fungi including Fusarium sp., Macrophomina phaseoll, Pythium sp., and Rhizoctonia solani have been held responsible for seed and seedling rot. The disease can be easily recognized by poor germination and stand. There is an initiation of rotting of seed because of the fungi. The seed. lings also rot and finally die resulting in a poor stand.
Control Measures;
To control the speed and seedling rot, the best way is to get clean seed from a healthy crop and treat it with fungicides like Thiram (0.25%) or Captan (0.25%).
f) Cercospora Leaf Spot;
This disease is caused by two species of Cercospora fungus. It is the most important fungal disease of the moong crop. In the diseased condition, small round spots, violet-red in color may be observed. These spots can be recognized by their grey-colored center. Such spots are also visible or pods and the affected pods become blackened.
Control Measures;
Spray Dithane Z-78 or Dithane M-45 at the rate of 2 kg in 1000 liter of water per hectare. or Apply Carbendazim 500 g/ha or Mancozeb 1000g /ha The first spray should be given as soon as the initial symptoms of the disease are visible. This should be followed by a second spray 10 days later.
This disease is caused by a fungus, Colletorichum capsici. The disease is initially characterized by the production of dark brown circular spots. Later the spots increase in size by developing concentric ridges. The areas in between the concentric ridges remain ash-colored. The infection may also spread to pods where dark-colored spots are visible on them.
Control Measures ;
This disease can be controlled by planting healthy seeds. Fungicides like Dithane M-45 or Dithane Z-78 are also effective. Spray 2 kg of either of these fungicides in 1000 liters of water per hectare. or Apply Mancozeb 2g/lit or Carbendazim 0.5g/lit.
h) Charcoal Rot ;
This disease is caused by a fungus, Macrophumina phaseoli. This disease is more prevalent in Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, and Orissa. The disease is characterized by the rotting of roots and stems of the plant. Usually, the plants get infected after a month of sowing and die because of the rotting of roots. The rotting starts from the roots and proceeds towards the stem where reddish-brown to black-colored spots are formed near the soil surface. The affected stem later turns black.
Control Measures;
This disease can be controlled by treating the seeds before sowing with Brassicol (0.25%). It is advisable to follow a crop rotation with such crops as jowar or bajra which helps to reduce the fungus in the soil.
Insect Pests Manegement;
a) Hairy Caterpillar;
Three species of hairy caterpillars may cause severe damage to the moong crop, by eating away all the green matter of the leaves. The adult moths of these caterpillars lay eggs in large clusters and the young larvae are also congregated. The red hairy caterpillar may damage the crop at the seedling stage. Damage can be very severe. Sometimes re-sowing may be necessary.
Control Measures;
(1) Collect and destroy the eggs and young larvae.
b) Galerucid Beetle ;
This beetle is one of the important pests of moong. The insect avoids sunlight and causes more damage during dusk and night. It hides under debris and loose soil during the daytime. The adult beetle stipples the leaves with small and more or less circular holes.
Control Measures;
A basal application of Temik 10% granules or Thimet 10% granules at the rate of 10 kg per hectare is effective.
c) Leaf Hopper;
The adults and nymphs of this hopper suck the juice from the leaves. Generally, the insect sucks sap from the lower surface of the leaves but also occasionally from the upper surface. As a result of sucking the sap. the leaves turn brown and curl from the edge.
Control Measures;
d)Jassids;
The adults and nymphs of this insect suck the sap from the leaves and the damage is more severe when the plants are young. The leaves are crumpled and the plants look sick.
Control Measures;
The control measures suggested for leafhoppers also hold good for protecting the crop from this insect.
Harvesting and Threshing of Green Gram (Moongbean)
- The shattering of pods is a great problem with this pulse. Therefore, picking should be done as soon as the pods mature.
- Harvesting should be completed in two to three pickings. The varieties which are quite synchronous in maturity, require only two pickings, or sometimes the whole crop may be harvested with a sickle.
- The pods or whole crop after complete drying should be threshed manually.
The Yield of Green Gram (Moongbean)
A well-managed crop, as indicated above, may yield 12 to 15 quintals of grain per hectare.






Pingback: Cultivation of Ginger - Agrovista-Farming