Insect Pest Management in Rice Crop for a Bumper Harvest
Insect Pest Management in Rice Crop for a Bumper Harvest;
Rice (Oryza sp.) is the major staple food of over half of the World’s population. Rice is consumed by more than 2 billion people across the globe for their daily dietary requirements.
Various factors that influence the production losses are as follows;
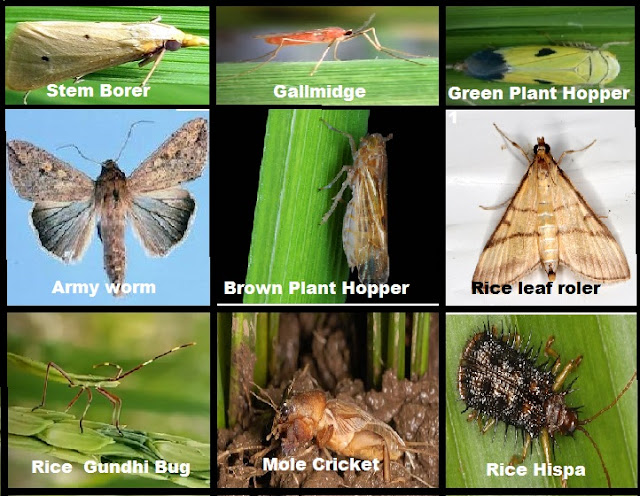
1) Rice Stem Borer; (Scirpophaga incertulas)
Control Measures;
4) Survey the field and if 5 % or more dead hearts are seen then immediate spraying is required
2) Gall Midge (Orseolia oryzae);
1) In midge-affected plants, regular tillers are transformed into a tubular gall resembling the leaf of an onion.
Control Measures;
If there are 5 % or more affected tillers per square mere adopt the same measures as suggested for the control of stem borer.
3) Rice Hispa (Dicladispa armigera) ;
The adults of rice hispa insects scrap on the epidermis or upper surface of the leaf blade, leaving only the lower epidermis the damaged areas can be seen with white streaks parallel to the midrib. Grubs mine between two epidermal layers producing irregular longitudinal white mines
Control Measures
It can be controlled by the spraying of insecticides; like; Triazophos 40 EC @ 400 ml/ha or Phosalone 35 EC @ 850 ml/ha or Chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 1,500 ml/ha or Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1,200 ml/ha or Ethofenprox 10 EC @ 450 ml/ha or Fipronil 5 SC @ 600 ml/ha
1) Caterpillars of this pest cause damage by folding the leaf blades into tubular structures and feeding on the green leaf tissues within these structures.
Control Measures
1) one damaged leaf is seen in each hill, protect the crop by spraying Phosalone 35 EC 1500 ml/ha or Chlorpyriphos 20 EC 1250 ml/ha or Carbaryl 50 WP 1.0 kg/ha or Acephate 75 % SP 666-1000 ml/ha or Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC 150 g/ha or Chlorantraniliprole 0.4% G 10 kg/ha or ronil 80%WG 50-62.5 g/ha or Flubendiamide 39.35% M/M SC 50 g/ha
4) Keep the bunds clean
5) Swarming Caterpillar; (Spodoptera mauritia )
This pest causes severe damage in nursery heds. Newly hatched larvae cut leaves and cause plants to look sickly with withered tips. Older larvae feed voraciously and cause almost complete defoliation. These larvae migrate from fields and do damage at night.
Control Measures
In case of moderate to severe damage, Drain the water from the nursery and spray chlorpyriphos 20 EC 80 ml during the late evening
6) Army Worm or Earhead Cutting Caterpillar; (Mythimna separate )
The caterpillars are greenish-brown in color with a pair of prominent dorsolateral stripes on the body. Larvae feed voraciously on leaves, resulting in skeletonizing of leaf blades. They have a climbing habit and cut panicles from the base and do damage at night. The insect migrates from one field to another.
Control Measures
Spray any of the given insecticide like Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1,600 ml/ha or Chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2,000 ml/ha or Carbaryl 50 WP @ 1,500 g/ha or Phosalone 35 EC @ 1,100 ml/ha
7) Gundhi Bug; (Leptocorisa oratorio )
Both nymphs and adults cause damage by sucking the plant sap and particularly the milky juice of the developing grains in the early morning hours or at dusk. The grains are then either empty or partly filled and shriveled
This pest is popularly known as Gundhi bug because it produces a pleasant smell when touched or disturbed.
Control Measures
In this case, there are five or more insects per metre row length, as a control measure apply Carbaryl 50 WP @ 1,500 g/ha during afternoon hours. or Dust Malathion or Carbaryl @ 30 kg of the formulation/ha
8) Mole Cricket ( Gryllotalpidae )
This is a problem with raised nursery beds and in upland fields. Flooded rice becomes infested only when water is removed from the field. The adults of this pest feeds on the tender roots and lower portions of the plant below the ground. They may kill the plant by cutting at the base.
Control Measures
2) Encourage biological control agents: sphecid wasp, carabid beetle, nematodes, and fungus; mole crickets eat each other when they are together because of their cannibalistic behavior
3) It can be control by the poisinous insects by baits that are made by mixing moistened rice bran and insecticide and placing it along the entire bunds of the rice field or drier areas of the field
9) Green Leaf Hopper ( Nephotettix virescens )
Generally, leafhoppers feed on leaves and upper parts of plants by sucking cell sap. It also transmits tungro virus disease. The disease is Characterised by slight stunting and reduced tillering. Young leaves are often mottled with pale-green to whitish stripes. Infected plants posses only few light spikelets.
Control Measures;
It can be control by the application of the insecticides like Imidacloprid 200 SL @ 125 ml/ha or Thiamethoxam 25 WG @ 100 g/ha or Ethofenprox 10 EC @ 500 ml/ha or Acephate 50 WP @ 950 g/ha or Carbaryl 50 WP @ 900 g/ha
10) Brown Plant Hopper ; (Nilaparvata lugens)
1) These are of two types-white backed plant hopper and brown plant hopper (BPH)
Control Measures;
In case plant happens population reaches five to ten per bill, treat the stop with Spray of Imidacloprid 200 SL @ 125 ml/ha or Thiamethoxam 25 WG @ 100 g/ha or Ethofenprox 10 EC @ 500 ml/ha or Acephate 50 WP @ 950 g/ha Carbaryl 50 WP @ 900 g/h Care should be taken to direct the sprays towards the base of the plants, particularly for the control of plant hoppers as they remain on husal part of the plants.













Pingback: Dry or Semi Dry Upland Rice Cultivation in India - Agrovista-Farming