Insecticide Formulations and their Calculation ; A brief Information
Insecticide Formulations and Their Calculation; A brief Information
An insecticide formulation is a mixture of chemicals (Active + Inert or inactive ingredients) that effectively control a pest population. Formulating an insecticide involves processing it to improve its storage, handling, safety, application, or effectiveness.
Few accessory substances are used in formulating a pesticide, such as
The terminology used in Insecticide Formulations;
1. Dry Formulations
These formulations can be used in the dry form only.
(a) Powders
These are ground materials of insecticides, which are used as such without mixing any diluent such as
(1) Powder of Derris roots;
The roots of D. elliptica possess rotenone, a strong insecticide, and fish poison. also, known as derris powder and tuba root (in Indonesia), it was formerly used as an organic insecticide used to control pests on crops such as peas.
(2) Powder of Pyrethrum flowers.
Pyrethrum is also the name of a natural insecticide made from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium and Chrysanthemum coccineum. Its active ingredient is pyrethrins.
(b) Dust;
1) Dust is a finely ground material designated by ‘D’.The Particle’s size of dust range between 1 and 400 i.e.
2) When an inert diluent is mixed with a small quantity of concentrated poison, then the mixture is called dust.
4) The diluent (soapstone, pyrophyllite, lime, or clay) does not react with the ingredient of the poison.
4) Insecticide dust is especially effective in killing crawling insect pests (bed bugs, roaches, fleas, etc.)
|
Advantages of Dust Formulations |
Disadvantages of Dust Formulations |
|
a) Long-lasting b) they often do not break down c) Low odor – Easy to apply d) Not absorbed into surfaces and are readily picked up by pests e) If spilled, dust can be easily cleaned up |
a) Readily become airborne and can contaminate non-target surfaces b) Readily inhaled by the applicator, technicians should wear a respirator for application c) Can be abrasive, and eye protection should be worn |
The particles of granular insecticides are larger than the particles of dust. The granules vary from 0.25 to 24 mm in diameter. Such insecticides consist of inert material with the poisons absorbed onto them. Granular formulations of certain systemic insecticides are available for the control of leafhoppers. planthoppers, aphids, thrips, etc.
|
Advantages of Granular Formulations |
Disadvantages of Granular Formulations |
|
a) Low drift b) Ease of application c) Long residual life outdoors
|
a) Water is required to release the insecticide b) Although some manufacturers are overcoming this aspect c) Limited to outdoor application d)Application equipment must be calibrated often |
Certain stomach cum contact poisons kill the pest through stomach poisoning but they may kill useful insects (predators) also due to contact action. This contact action of such insecticides can be removed by coating them with an inert fine dust so that the poison particles remain coated all over and do not kill useful insects by contact. However, when eaten up by insect pests they kill them by stomach poisoning such as zeilin.
(e) Insecticide-fertiliser mixture
Mostly granular insecticides are mixed in the fertilizers to form an insecticide fertilizer mixture. This mixture can be applied to the plants, will control the soil insects and at the same time, it will provide nutrition to plants.
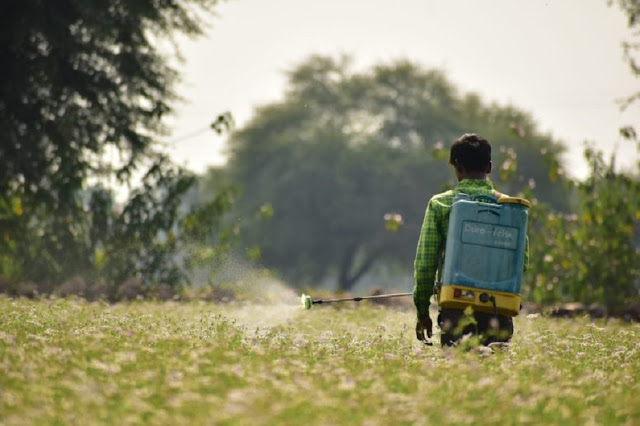
2. Formulations for use as Liquid Sprays
Many organic insecticides are not soluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents (amyl acetate, carbon tetrachloride, refined kerosene monochlorobenzene, etc). Solvents also possess some insecticidal properties and are phytotoxic at high concentrations. Therefore it is essential to know that solutions dissolved in solvents are phytotoxic and should not be applied to plants. These solutions can be used against household pests, mosquitoes, and other aquatic insects.
(b) Emulsifiable concentrates (EC)
This type of formulation is more commonly used. It is a mixture of toxicants; a solvent and an emulsifying agent. In the market, these are available as EC. To spray this insecticide some amount of water is added to make an aqueous suspension. The insecticide when sprayed, the solvent evaporates leaving the toxicant with water. Water also evaporates after some time. More common insecticides of this type are, Endrin 20% EC. Malathion 50% EC etc.
|
Advantages of Emulsifiable concentrates (EC) |
Disadvantages of Emulsifiable concentrates (EC) |
|
a) Bind well to fabrics and fibers in the carpet. b) Easy to mix and use c) Spreads evenly over the foliage d) Binds well to soil particles |
a) Mild to strong odors b) Absorption onto porous surfaces c) Potential burning of plant material d) Errors in mixing the concentrate with water e) Some surfaces such as plastic or tile may be damaged f) Can easily penetrate the skin |
This formulation is termed U.L.V. or L.V.C. because this is not diluted with water but applied as such in a highly concentrated form. Low-volume concentrates are passed through specialized nozzles into a blast of air generated by a blower fan. The air serves as a diluent. This type of formulation is much used for ‘aerial spraying’, for example, L.V.C. of Malathion, L.V.C. of Sevin.
(d) Suspension
This is the formulation in which the active material is suspended as solid particles.
(e) Foam Sprays
The spray mixture of insecticide, when passed through special foam nozzles converts the spray into foam.
(f) Mist Sprays
Sprays with very small droplets are known as mist sprays.
(g) Water-dispersible powder
WDP may contain 15 to 95 percent toxicant. Most of the insecticides are insoluble in water, and are mixed with carriers. These carriers are soluble or partly soluble in water. This mixture of toxicant and carrier is known as W.D.P.
|
Advantages of Water dispersible powder (WDP) |
Disadvantages of Water dispersible powder(WDP) |
|
a) No oil-based solvents b) Low to no odor c) Little hazard of burning plants d) Little hazard of penetrating skin e) Do not absorb into porous surfaces, when water evaporates f) powder sits on the surface and is readily picked up by insects |
a) Inhalation of particles while mixing concentrate b) Constant agitation of suspension prior to and during application c) Large mesh strainer must be used (>50 mesh) in sprayers d) Pumps and nozzles can be damaged by abrasion of the particles e) Visible residues can occur on dark surfacesh |
|
Advantages of Insecticide Aerosols |
Disadvantages of Insecticide Aerosols |
|
a) Ease of use b) Ease of storage c) No dilution or storage of concentrates |
a) Expensive b) Odor of solvents c) Atomized droplets are easy to inhale and drift to non-target surfaces |
3. Fumigants (Gaseous Formulations)
As described earlier the toxicants in the gaseous form are known as fumigants. These may be used in bins, houses, godowns, ships, aircraft, and soil, etc. Most of the fumigants are inflammable, therefore they are mixed with a non-inflammable gas such as carbon tetrachloride. Some of the common fumigants are listed below.
|
Advantages of Fumigants |
Disadvantages of Fumigants |
|
a) Toxic to a wide variety of pests b) Good penetration of target areas c) Single treatment will usually kill all pests in the treated area |
a) Treated area must be closed or tented to prevent gas from escaping b) Highly toxic to people |







I’d add some other ideas that contradict this. With your permission…?