Advantages and Features of the Drip or Trickle Irrigation System
Advantages and Features of the Drip or Trickle Irrigation System
How Drip system works ;
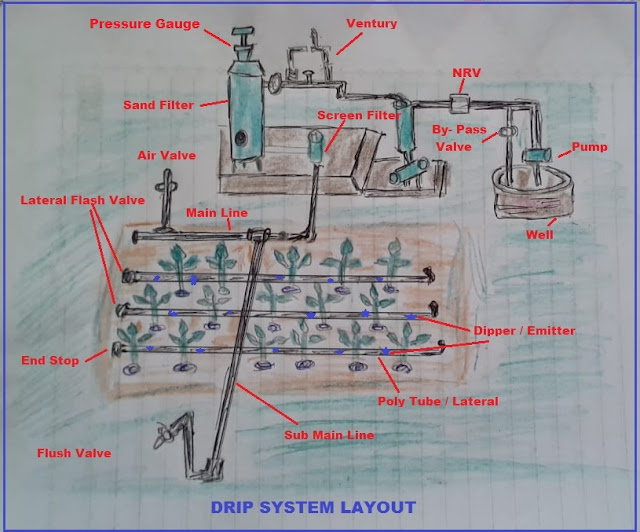
Drip System Layout;
|
Major Components of Drip Irrigation System |
|||
|
1 |
Pump station. |
6 |
Pressure gauge |
|
2 |
By-pass-assembly |
7 |
Mains / Sub-mains |
|
3 |
Control Valve |
8 |
Laterals |
|
4 |
Filtration system |
9 |
Emitting devices |
|
5 |
Fertilizer tank /Venturi |
10 |
Microtubes |
Suitable crops for Drip Irrigation System;
|
1 |
Orchard Crops |
|
|
Papaya, Aonla, Litchi, Watermelon, |
||
|
Muskmelon etc. |
||
|
2 |
Vegetables |
|
|
Pumpkin etc. |
||
|
3 |
Cash Crops |
Sugarcane, Cotton. Arecanut, Strawberry etc. |
|
4 |
Flowers |
Rose, Carnation, Gerbera, Anthurium, |
|
|
||
|
5 |
Plantation |
Tea, Rubber, Coffee, Coconut, etc. |
|
6 |
Spices |
Turmeric, Cloves, Mint etc, |
|
7 |
Oil Seed |
|
|
8 |
Forest Crops |
Teakwood, Bamboo, etc. |
How the Different Crop Response under Drip Irrigation System ;
Advantages and disadvantages of drip irrigation ;
A) Advantages:
1) Drip irrigation system minimizes the losses of fertilizer and nutrient loss due to localized application It also reduced leaching.
2) It enhances the water application efficiency under well-managed conditions.
3) Leveling of the field is not so important under the drip irrigation system.
4) Under the drip irrigation system the fields that possess irregular shapes can be easily accommodated.
5) Use of recycled non-potable water is very safe in Drip irrigation.
6) Moisture levels within the root zone can be maintained at field capacity.
7) Soil type has no role in the frequency of irrigation.
8) It reduces the loss of soil due to erosion.
9) It suppresses weed growth.
10) Under drip irrigation the water distribution process is highly uniform and the output of each nozzle can be easily controlled.
11) Labor cost in a drip irrigation system is quite less in comparison to the other irrigation methods.
12) Water supply can be easily regulated by regulating the valves and drippers.
13) Fertigation can easily be performed without waste fertilizers.
14) In the Drip irrigation system there is less chance of disease occurrence because most of the time foliage remains dry
15) Drip irrigation systems usually work under lower pressure in comparison to other types of pressurized irrigation hence it reduces the cost of energy.
B) Disadvantages:
1) Initial cost can be more than sprinkler systems.
2) The high temperatures during the summer can affect the tubes used for drip irrigation, shortening their usable life.
3) Clogging may take place due to poor filtration of water and the improper maintenance of the equipment
5) Drip irrigation plays zero role in herbicides spray or top-dressed fertilizers for this there is a need for sprinkler irrigation
6) In the drip irrigation system tape causes extra cleanup costs after each harvest. Farmers are required to plan for drip tape winding, disposal, recycling, or reuse.
7) If the drip irrigation is not installed properly there is a more chance of waste of water, time, and harvest. Therefore drip irrigation systems need a careful study of all the important factors Viz; land topography, soil type, water, crop, and agro-climatic conditions, and suitability of drip irrigation system and its components.
8) In the case of lighter soils subsurface drip irrigation system may not be able to wet the soil surface for germination. Hence it requires careful consideration in contrast to the installation depth of the system.
9) Drip systems are designed for high-efficiency uses, hence there is little or no leaching fraction. In the absence of sufficient leaching, salts applied with the irrigation water may be accumulated in the root zone, most commonly at the edge of the wetting pattern. While on the other hand, drip irrigation systems avoid the high capillary potential of traditional surface-applied irrigation, which can draw salt deposits up from deposits below.
10) Damage of the PVC pipes is often occurred due to rodent activity, and the replacement of the entire damaged tube increases the expenses.
11) Drip irrigation systems are useless for controlling the damage that occurred due to the tonight frosts (like in the case of sprinkler irrigation systems)